Tree-based Visualization and Optimization for Image Collection
Xintong Han, Chongyang Zhang, Weiyao Lin, Mingliang Xu, Bin Sheng, and Tao Mei
Department of Electronic Engineering,
Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China
wylin@sjtu.edu.cn
The visualization of an image collection is the process of displaying a collection of images on a screen under some specific layout requirements. This paper focuses on an important problem that is not well addressed by the previous methods: visualizing image collections into arbitrary layout shapes while arranging images according to user-defined semantic or visual correlations (e.g., color or object category). To this end, we first propose a property-based tree construction scheme to organize images of a collection into a tree structure according to user-defined properties. In this way, images can be adaptively placed with the desired semantic or visual correlations in the final visualization layout. Then, we design a two-step visualization optimization scheme to further optimize image layouts. As a result, multiple layout effects including layout shape and image overlap ratio can be effectively controlled to guarantee a satisfactory visualization. Finally, we also propose a tree-transfer scheme such that visualization layouts can be adaptively changed when users select different “images of interest”. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach through the comparisons with state-of-the-art visualization techniques.
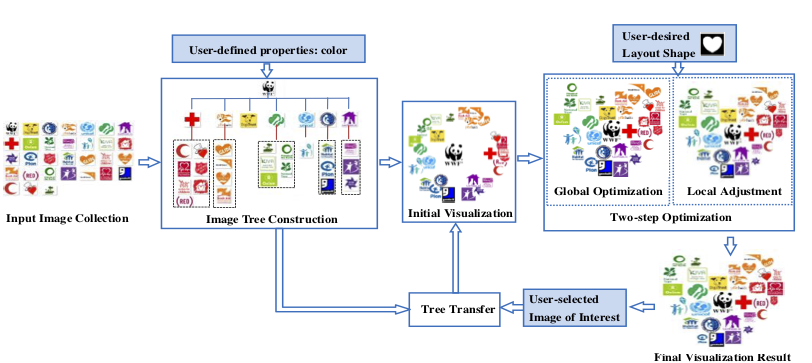
This figure illustrates the overview of our proposed approach. Our approach mainly includes four components. First, the “image tree construction” component is used to organize images into a tree structure such that user-desired visual or semantic correlation among images can be well embedded. After that, we need to project this tree into a visualization space to create a visualization layout. Since simple projection cannot effectively create arbitrary layout shapes or avoid image overlaps, our approach introduces two components to transfer a tree into a final visualization layout: first, projection methods are applied to project a tree to create an initial visualization layout (i.e., the “initial visualization” component) [5], [13]. Then, the “two-step optimization” componentfurther updates and optimizes the initial layout through the “global optimization” and “local adjustment” steps. Since projection methods can reflect correlations of a tree in the layout space while two-step optimization can effectively control layout effects, by combining these components, both the desired image correlations and the layout effects can be guaranteed in the final layout. Finally, if a user selects his/her image of interest, the “tree-transfer” component will transfer the tree structure accordingly. And this transferred tree will then go through the initial visualization and the two-step optimization components to achieve the updated layout.
Figure 1
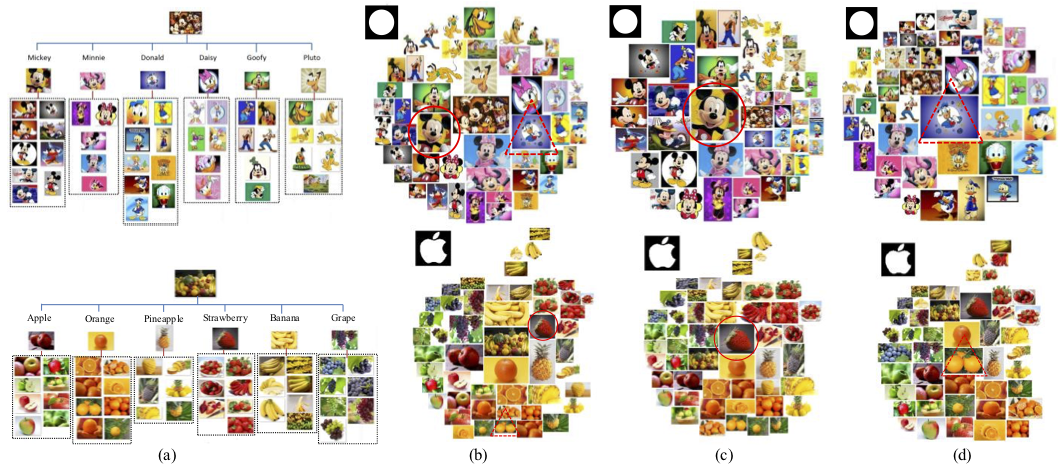
Top: The image collage of a photo album for "Mickey Mouse and Donald Duck". Down: The image collage of fruit images grouped by different kinds of fruits. (a): The constructed image trees; (b): The visualization layouts by our approach; (c): The updated layouts by the tree transfer scheme when the solid circle images are selected as the image of interest; (d): The updated layouts by the tree transfer scheme when the dashed triangle images are selected as the image of interest.
Table Ⅰ
The average user score and confidence interval for different approaches.
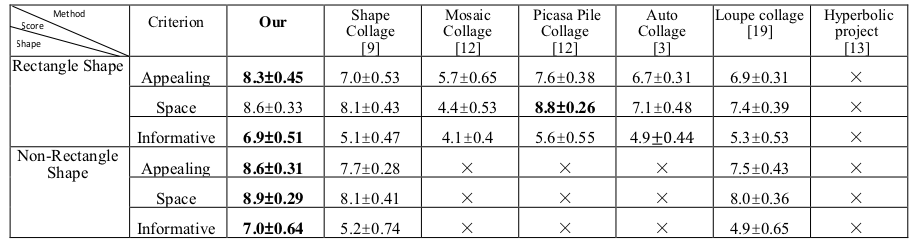
This table shows the average user scores for different methods together with the 95% confidence interval [43]. Besides, it shows the Wilcoxon signed-rank test results [42] by comparing the user scores of our approach with each of the compared method. This indicates the existence of significant user-score differences between our approach and the compared methods.
Institute of Media, Information, and Network (MIN Lab)
沪交ICP备20160059